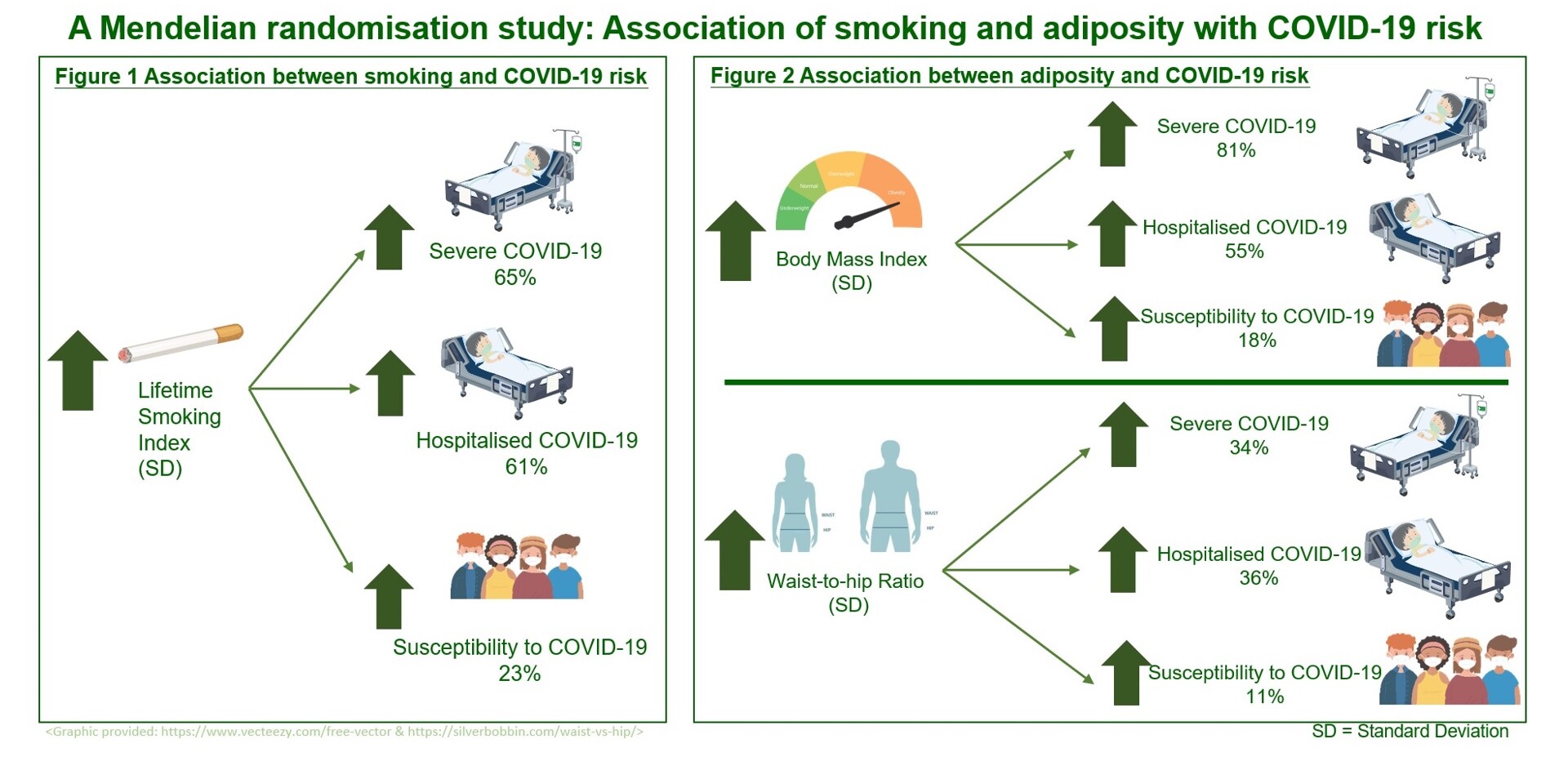
Researchers from CU Medicine and the School of Public Health at HKUMed, confirmed smoking, obesity and lower socioeconomic position (SEP) likely increase the risk of contracting mild to severe COVID-19, using data from large scale genome-wide association studies. The research team found that smoking, obesity and lower SEP likely increase the risk of COVID-19.
For example, one standard deviation increase (SD) of body mass index (BMI) likely
- increases risk of severe COVID-19 by 81%
- Increases risk of COVID-19 hospitalisation by 55%
- increases risk of contracting COVID-19 by18%
The research team also explored whether ACE2 mediates any of these detrimental effects. ‘SARS-CoV-2 enters the host cells via ACE2. Recently, various therapeutic approaches have been developed for COVID-19 patients with the utilisation of ACE2-modulating medications to effectively control viral entry. Our findings will enhance research into several therapeutic targets for COVID-19 treatment,’ said Professor Kwok Kin-on, Assistant Professor, the Jockey Club School of Public Health and Primary Care, CU Medicine.
Full article: https://bit.ly/3Fs4Q2L
Details: https://bit.ly/3VVZvYD
